As of now, the main categorization criteria for proxies are the list of functions, which they perform, and goals, for which they are created.
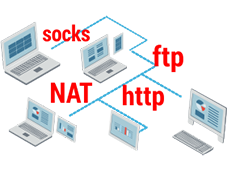
1. HTTP/HTTPS is believed to be the most common type with port numbers 80, 8080, 3128 (other numbers are less common). In turn, HTTP proxies are subcategorized according to the degree of anonymity:
- transparent proxies redirect all traffic or parts of it implicitly with the help of a router. They do not hide users’ actual IP addresses.
- anonymous proxies, unlike transparent ones, do hide users’ actual IP addresses and do indicate that a proxy is being used.
- distorting proxies, apart from providing anonymity, share fake (distorted) IPs, as they are used for misleading, targeting and neutralizing potential felons in a safe mode.
- elite proxies, along with the functions performed by the previous subtypes, ensure complete anonymity, as there is nothing to indicate that a proxy is being used to access a resource.
2. SOCKS is a kind of proxy server, which directs all client data to the targeted server without changing or supplementing it. In this case, a web server identifies a SOCKS proxy as a client and ensures anonymity a priori. In most cases, it uses Port 1080 and Port 1081. SOCKS proxies are subdivided into SOCKS4, SOCKS4a, and SOCKS5.
3. FTP is a kind of proxy server, which is used for operating file cabinets.
4. CGI proxies (anonymizers) make a separate category of proxy servers, as they are actually sites intended for surfing the web anonymously. They add anonymizers’ domains to URLs, so that all data packages be automatically directed via the proxy server.
Apart from the types mentioned above, there are proxy types, which are popular among individual users:
- for ОС Windows: CoolProxy, Microsoft Forefront Threat Management Gateway, Traffic Inspector, UserGate, WinGate (they use an open code, but the software itself is not free – proprietary proxies); Eserv, HandyCache (not free);
- for ОС Linux - Ideco ICS;
- multiplatform proxies: Kerio Control (proprietary); Squid, TOR (open source)
Back to articles
 Main types of proxy servers
Main types of proxy servers